All About Heat Sinks- Types & Functions
Heat sinks are one of the common heat management systems in technology. They are so universal that we often forget their contribution in maintaining the systems. Let's discuss some basics on heat sinks and their importance.
What is a heat sink?
A heat sink is a safety device that is used to take the heat away from the device. It accomplishes this task by increasing the working surface area and allowing a low temperature fluid to pass through the enlarged surface area and hence decreasing the overall temperature.
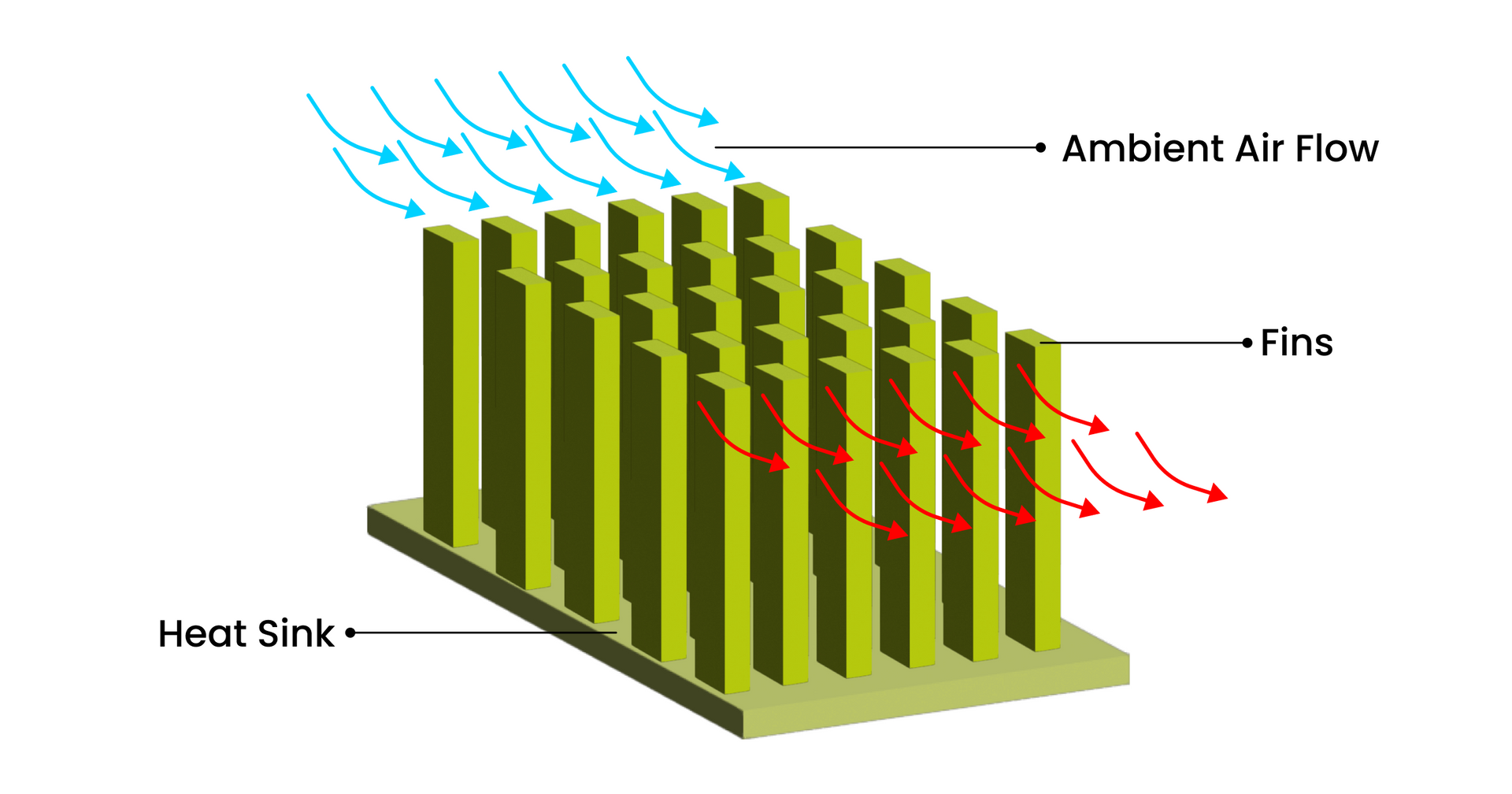
How does a heat sink work?
The working of heat sink can be explained in 4 simple steps
Source generates the heat: The source is any system that generates heat which requires it to be removed for proper working.
Heat transfers away from source: Heat is moved to heat sink from the source through natural conduction, which is directly impacted by sink’s thermal conductivity. This is made possible by using material of high conductivity like copper and aluminum in the sink.
Heat distributes throughout the sink: Heat travels throughout the heat sink via natural conduction, moving across the thermal gradient from high temperature to low temperature, which means it will be hotter at the side of source and cooler at the other extreme of the sink.
Heat moves away from heat sink: It depends on the sink’s temperature gradient and its working fluid-mostly air or electrically nonconductive liquid.
- The working fluid runs across the surface of the heat sink using thermal diffusion and convection to move heat away from the surface into the surrounding environment.
- It relies on temperature gradient so no convection and heat removal will occur if the surrounding temperature is not cooler than the heat sink.
- The total surface area of the heat sink is also important as the large surface area enables better thermal diffusion and convection.
What are the types of heat sinks?
There are three types of heat sinks – Active, Passive & Hybrid.
Passive heat sink- Passive sinks rely on natural convection as they rely on the ability of hot air to float and causes the airflow to be generated across the heat sink, they do not require any secondary method of heat removal. But passive heat sinks are not effective in removing heat from system as active heat sinks.
Active heat sink- Active sink utilizes forced air commonly generated by a fan or blower to increase the fluid flow in hot areas.
Hybrid heat sink- Hybrid heat sinks combine both the active and passive characteristics. Such configurations are less common and use control systems to cool. When the system is operating at cooler levels the forced air is inactive and thus cooling the system passively. Once the source reaches the higher temperature, the active cooling mechanism engages to increase the cooling capacity of sink.
Heat Sink Compound
Heat sink compound or thermal grease is a stick paste that is used as an interface between CPU heat sinks and heat sources. The mechanical heat sink is kept over the CPU, heat is drawn from the CPU to mechanical sink through fins, where the fan blows to dissipate the excess heat.
Heat sinks play a critical part in dispersing the heat away from CPU and avoid overheating. Heat sinks are often overlooked for the helpful devices they are. Us Electronics provide with the best solutions for heat sinks.